Anatomy of Male Groin Area: Muscles, Functions, and Conditions
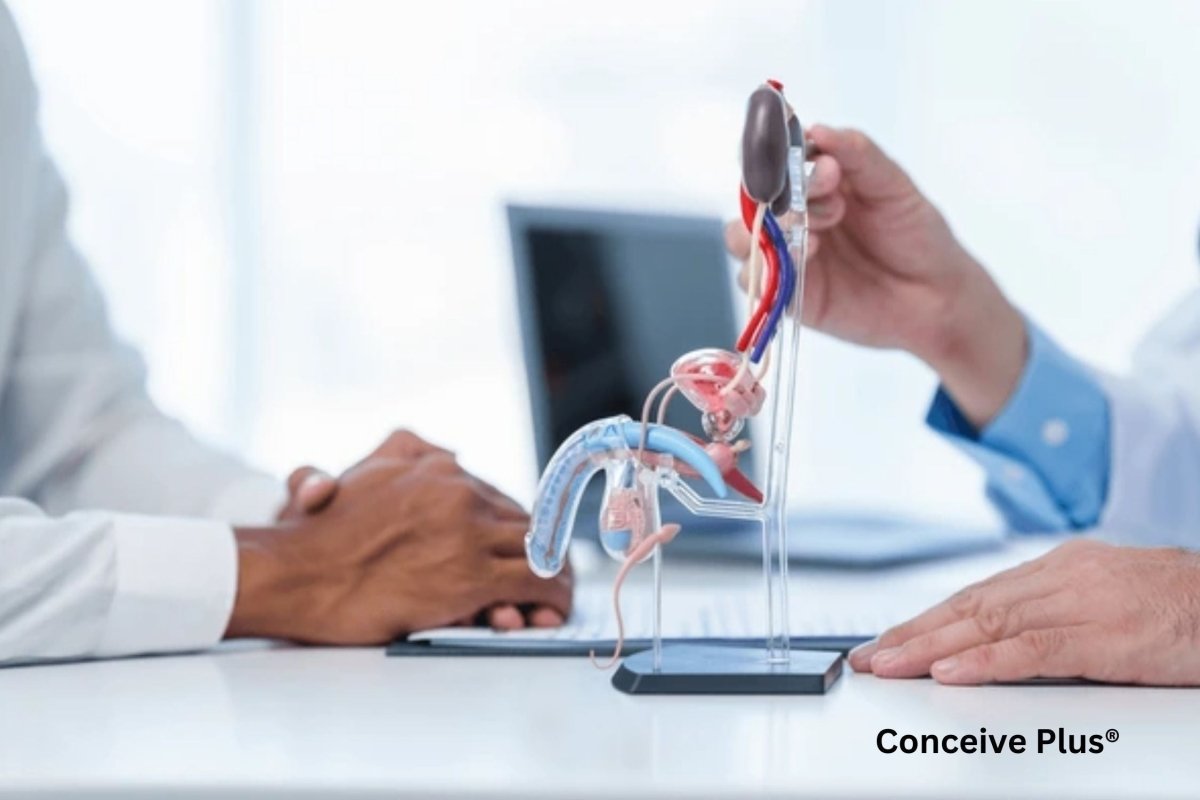

The anatomy of male groin area consists of bones, muscles, and soft tissues which connect the lower abdomen to the legs. Each part helps protect the organs near the groin and supports everyday movements.
Strong and healthy structures in this region help maintain balance, mobility, and reproductive function. You might ask, why do I need to know about the anatomy of the groin? Studying the anatomy of male groin area helps you recognize how your body supports movement. It also helps you take proper care and pay early attention when problems occur.
Anatomy of the Male Groin Area
The male groin is a part of the body where the abdomen meets the thigh. Several components are involved in this anatomy that work together for support and movement.
-
Bones and Muscles
The muscles and bones you will see in any male groin diagram give it its functional structure. The pelvic bone is one of the main bones in this area. The muscles here include the hip adductors which bring the legs together and help stabilize the body when you stand or walk [1]. Besides assisting in walking, these muscles help protect the inner parts of the groin.
-
Soft Tissues and Other Structures
In the groin region, soft tissues also play important roles. One major soft tissue structure is the inguinal canal [2]. This is a small tunnel where important tissues, such as the spermatic cord, pass. The spermatic cord carries blood vessels, nerves, and the vas deferens.
The vas deferens transports man sperm from the testes to the urethra, where they exit the body during ejaculation. The anatomy of the male groin area also includes lymph nodes and blood vessels. Lymph nodes collect extracellular fluid and fight infections, while blood vessels move blood to and from the groin region.
For an even deeper understanding of male body anatomy—especially the functions of the testicle and scrotum—be sure to check out our article "Male Body Anatomy Testicle and Scrotum Function."
Functions of Groin Components
The parts of the groin region have clear jobs that keep the body working well. Their roles include:
-
Structural Support
The bones and muscles in the groin area give the body strength and support. They hold up the upper body and help you stay upright. Without them, it would be hard to keep your balance or move properly.
These parts of the body work all the time, especially when you're doing simple things like standing, walking, or getting up. Having strong bones and muscles in this area makes daily movements easier and helps you stay steady on your feet.
-
Movement and Flexibility
The groin muscles play a big part in how we move. You use them when you walk, run, jump, or turn quickly. If these muscles are flexible, you're less likely to get hurt during sports or other activities. They help your body move freely and stay strong.
-
Reproductive and Urinary Functions
In addition to movement and support, the groin area also plays a major role in reproductive and urinary functions. The inguinal canal, which is a part of this region, helps protect the spermatic cord [3]. This cord is essential for carrying sperm, which is vital for male fertility and reproduction. The nearby structures also help in the passage of urine from the bladder through the urethra.
If you're curious about how pregnant woman anatomy adapts throughout the reproductive process, be sure to check out our article "Pregnant Woman Anatomy: From Conception to Delivery" for a comprehensive exploration.
Conditions Affecting the Groin Area
Some conditions can cause problems in the groin. These conditions can affect everyday activities and lead to several complications.
-
Inguinal Hernia
Inguinal hernia is one of the most common conditions associated with the groin. Inguinal hernia is when a small part of the intestine pushes through the inguinal canal or a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall [4].
It can cause pain and discomfort, especially when lifting heavy objects or during physical activity. In most cases, the fixation of an inguinal hernia involves a simple surgical procedure.
-
Testicular Torsion and Other Issues
Another serious condition related to male groin anatomy is testicular torsion [5]. This occurs when the spermatic cord twists and cuts off blood flow to the testicle. Testicular torsion causes sudden and severe pain in the groin region.
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency and needs immediate treatment. Other conditions, such as infections or strains in the muscle, may also affect the groin. These problems can cause pain, swelling, or tenderness and are a risk factor for male fertility health and well-being.
-
Sports Injuries and Strains
The groin is used a lot during sports, so injuries in this area are common. Athletes often get muscle strains or small tears in the groin from quick movements or doing too much. These injuries can cause pain and make it hard to move. The good news is that with enough rest and the right care, most groin injuries get better over time.
The Bottom Line
The anatomy of male groin area includes muscles, bones, and soft tissues that work together to support the body. The components of the groin anatomy help with movement, balance, and important functions like reproduction.
Knowing how this area works can help you stay healthy and avoid injuries. It also makes it easier to notice problems early. Taking care of the groin through exercise and medical checkups is a smart way to protect your health and keep your body strong.
Resources Used
- Hrysomallis, C. (2009). Hip adductors’ strength, flexibility, and injury risk. The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 23(5), 1514–1517. https://doi.org/10.1519/jsc.0b013e3181a3c6c4
- Tuma, F., Lopez, R. A., & Varacallo, M. A. (2023, July 24). Anatomy, abdomen and pelvis: inguinal region (Inguinal canal). StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470204/
- TeachMeAnatomy. (2023, October 15). The spermatic cord - Course - Fascia - Contents - TeachMeAnatomy. https://teachmeanatomy.info/pelvis/the-male-reproductive-system/spermatic-cord/
- Hammoud, M., & Gerken, J. (2023, August 8). Inguinal hernia. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513332/
- Schick, M. A., & Sternard, B. T. (2023, June 12). Testicular torsion. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448199/