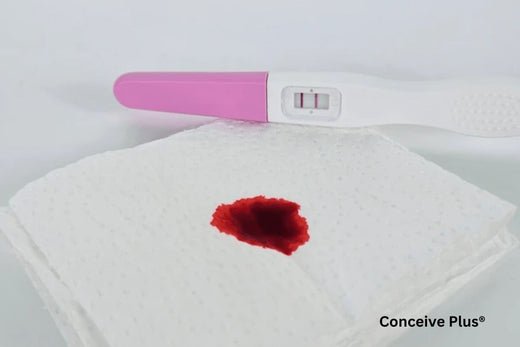
Is Light Spotting and Cramping In Early Pregnancy Normal?
Pregnancy brings many changes to a woman’s body. Some of these changes can be confusing for women, especially for those experiencing pregnancy for the first time.
Light spotting and cramping are common experiences during early pregnancy. In some cases, they are completely normal and result from pregnancy-related changes in the body [1]. However, in other cases, they can indicate some underlying issue that may risk the pregnancy.
In this article, we will understand the causes behind light spotting and cramping in early pregnancy days. We will also discuss when bleeding and cramping early pregnancy are normal and when they can be concerning, for which you require medical attention.
What Does Light Spotting During Early Pregnancy Mean?
Light spotting is a small amount of bleeding from the vagina. Women may notice such spotting multiple times during their menstrual period, but such spotting is also common in early pregnancy. One common scenario that may cause confusion is experiencing a missed period but spotting, which can sometimes occur in early pregnancy or due to other hormonal changes. Expectant mothers may notice pink, red, or brown spots on underwear or tissue. It is generally lighter than a period and doesn’t last long.
The causes of light spotting during early pregnancy can include the following:
-
Implantation Bleeding
Implantation is the phase when a fertilized egg implants into the uterine lining. Remember that pregnancy begins after implantation, and not fertilization. It usually occurs about a week or two after ovulation.
Implantation often causes light spotting, which is called implantation bleeding [2]. It usually has light pink or brown color and may last for a day or two. Reports show that 1 in 3 pregnant women experience implantation bleeding [2].

-
Hormonal Changes
Many sudden hormonal changes occur in the early days of pregnancy that may disturb the uterine lining and cause light bleeding. For example, after implantation, it takes time for the placenta to start producing progesterone hormone to sustain pregnancy [3].
It is possible to have lower levels of progesterone before the placenta starts functioning, which can lead to changes in the uterine lining and bleeding [4]. Estrogen and human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) hormones also start to rise during early pregnancy and may contribute to light spotting.
-
Cervical Sensitivity
Pregnancy hormones increase blood flow to the cervix and surrounding tissues. This increased blood supply in the early stages of pregnancy makes the cervix very sensitive [5].
Increased sensitivity means a high risk of irritation, especially during activities like intercourse. A pelvic exam in the early pregnancy days may also irritate the cervix and cause mild spotting.
-
Subchorionic Hematoma
Subchorionic hematoma is a condition where the blood collects between the uterine wall and the chorionic membrane [6]. It can cause light spotting and even heavy bleeding during early pregnancy. Subchorionic hematoma often resolves on its own and does not impact the health of the baby.

What Does Cramping During Early Pregnancy Mean?
Cramping during early pregnancy is often due to anatomical changes in the body to accommodate the growing baby. It may feel like mild period cramps and is usually not severe.
Common causes for cramping in early pregnancy days are:
- Implantation: As discussed earlier, implantation is the time when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterus. In addition to light spotting, implantation can also cause mild cramping which is usually short-lived and harmless.
- Uterine Changes: The uterus is the size of an orange before pregnancy and stretches to the size of a watermelon by the end of the pregnancy [7]. This expansion and growth in the size of the uterus to accommodate the growing baby can cause mild discomfort or cramping.
- Ligament Stretching: Two round ligaments, one on each side, connect the uterus to the body. These ligaments stretch during pregnancy due to the growing size of the uterus and cause pain. Ligamental pain is one of the common causes of abdominal pain that women experience during early pregnancy.
- Bloating and Constipation: Pregnancy causes an increase in progesterone levels to support the uterine lining. However, studies show that this hormone can also influence the digestive system and slow down digestion [8]. This is why bloating and constipation are some common symptoms in early pregnancy days. You may experience bloating as mild cramping in the abdomen.
When to Worry About Spotting and Cramping?
While cramps with bleeding early pregnancy is often normal, certain situations may require immediate medical attention. For example, bright red blood or large blood clots may indicate a miscarriage or other serious condition. Similarly, intense cramping or sharp pain in the abdomen may be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy or other complications.
If you experience fever and chills along spotting and cramping early pregnancy, it may indicate an infection. Such signs during pregnancy shouldn't be ignored and must be evaluated by a doctor to avoid serious pregnancy complications.
Other Concerning Signs in Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a delicate process, and many things can go wrong during the 9-month duration of pregnancy. Early identification of problems and expert guidance can help ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.
Here are some signs to watch for during pregnancy:
- Severe Nausea and Vomiting: Mild nausea and vomiting are not concerning as they are part of early signs of pregnancy in the body. However, excessive vomiting may indicate hyperemesis gravidarum, a condition that can lead to dehydration and nutrient deficiencies [9].
- Swelling in the Hands or Face: Pregnancy is the time when fluid retention in the body is higher, which may lead to mild swelling. However, sudden and severe swelling can be a symptom of preeclampsia, which is a serious pregnancy condition. You may also experience severe headaches and vision changes with preeclampsia.
- Reduced Fetal Movement: Fetal movements become prominent in the second trimester of pregnancy. These movements indicate that the baby is healthy. If there is a noticeable decrease in baby movements, you should report it to a doctor.
- Painful Urination: Frequent urination is a normal symptom of pregnancy, but if you experience pain while urinating, it can be an indication of a urinary tract infection (UTI). Early detection and management of UTIs are essential to limit their spread.
How to Support a Healthy Pregnancy?
Poor mother health can negatively impact the development of the baby and increase the risk of pregnancy complications. If you are an expectant mother, here are some tips that can help you improve your health to support a healthy pregnancy:
-
Eat a Balanced Diet
The nutritional demands of a woman’s body increase during pregnancy since it also has to nourish the baby [10]. She requires nutrients like folic acid, iron, calcium, and iodine to maintain her own health and to support the healthy development of the baby. A pregnant woman can get these nutrients by incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into her diet.
-
Take Prenatal Vitamins
A healthy diet is not always sufficient to fulfill the nutritional demands of your body during pregnancy. This is why experts recommend taking prenatal vitamins to avoid nutritional deficiencies that might risk pregnancy. Prenatal vitamins are dietary supplements that provide you with essential nutrients for pregnancy, such as folic acid, iron, calcium, iodine, and omega-3.
-
Stay Hydrated
Your body's fluid demand significantly increases during pregnancy. A study by the American Heart Association shows that a woman produces about 40% more blood than normal during pregnancy [11]. Drinking plenty of water can prevent dehydration and support your body’s increased fluid needs.
-
Exercise Safely
It is a misconception that exercise during pregnancy will always harm the baby, but in reality, moderate exercise can improve pregnancy health and lower the risk of complications during childbirth. For example, activities like walking or prenatal yoga can improve circulation and reduce stress. However, remember to refrain from intense exercises as they might harm the baby.
-
Listen to Your Body
If you feel unwell or notice unusual symptoms, such as persistent spotting with cramps that are more severe than normal, don't hesitate to consult your doctor. Keep in mind that early identification of pregnancy issues can help in better management and result in positive outcomes.
The Bottom Line
Light spotting and cramping are the two most common experiences for a pregnant woman in early pregnancy days. In most cases, cramping and spotting are a part of normal pregnancy related changes in the body and there is nothing to worry about.
However, if you start to notice symptoms like severe nausea, sudden swelling, painful urination along with spotting and cramping in early pregnancy, it is a good idea to share your symptoms with your doctor. Such signs can be an indication of serious conditions like hyperemesis gravidarum and preeclampsia that might risk the mother's health and the health of the baby during pregnancy.
Resources Used
- Soma-Pillay, P., Nelson-Piercy, C., Tolppanen, H., & Mebazaa, A. (2016b). Physiological changes in pregnancy. Cardiovascular Journal of South Africa/Cardiovascular Journal of Southern Africa, 27(2), 89–94. https://doi.org/10.5830/cvja-2016-021
- What is Implantation Bleeding? American Pregnancy Association. https://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-symptoms/what-is-implantation-bleeding/
- Shah, M. (n.d.). Low Progesterone and Its Impact on Early Pregnancy: NOVA IVF: Fertility Specialists. https://www.novaivf.com/blog/low-progesterone-and-its-impact-on-early-pregnancy
- Bataa, M., Abdelmessih, E., & Hanna, F. (2024). Exploring Progesterone Deficiency in First-Trimester Miscarriage and the Impact of Hormone Therapy on Foetal Development: A Scoping Review. Children, 11(4), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11040422
- Professional, C. C. M. (2024, August 27). Bleeding During Pregnancy. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/22044-bleeding-during-pregnancy
- Bondick, C. P., Das, J. M., & Fertel, H. (2023, July 31). Subchorionic Hemorrhage. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559017/
- ormal Uterus Size During Pregnancy. American Pregnancy Association. https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-health-wellness/uterus-size-during-pregnancy/
- Alqudah, M., Al-Shboul, O., Al-Dwairi, A., Al-U´Dat, D. G., & Alqudah, A. (2022). Progesterone Inhibitory Role on Gastrointestinal Motility. Physiological Research, 2, 193–198. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.934824
- Jennings, L. K., & Mahdy, H. (2023, July 31). Hyperemesis Gravidarum. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532917/
- Jouanne, M., Oddoux, S., Noël, A., & Voisin-Chiret, A. S. (2021). Nutrient Requirements during Pregnancy and Lactation. Nutrients, 13(2), 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020692
- Sanghavi, M., & Rutherford, J. D. (2014). Cardiovascular Physiology of Pregnancy. Circulation, 130(12), 1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.114.009029